Graves disease is caused by the over activity of thyroid gland. It is a type of hyperthyroidism caused by an autoimmune disorder. The over activity of the thyroid glands results in over production of thyroid hormones – Thyroxin (T4) and Tri-iodothyronine (T3). These hormones control the metabolism in the body. Imbalance of these hormones causes a serious metabolic condition known as thyrotoxicosis. This condition is caused by thyroid auto antibodies resulting in excessive secretion of thyroid hormones and an enlargement of thyroid glands known as Goitre.
Onset of the disease
Graves disease is most common among women and the age at the onset of this disease is 20 years. It is the commonest form of hyperthyroidism.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of Graves disease includes -
psychological problems like anxiety, concentration problems, insomnia, nervousness and tremor
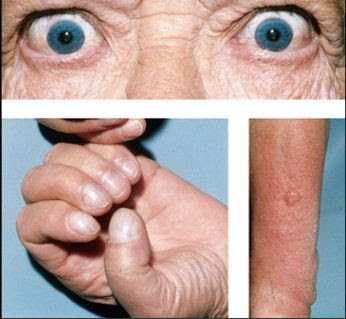
Physical Problems Like Breast enlargement in Men, Double vision, Exophthalmia (Protrusion of eye ball), tearing and eye irritation, Generalised weakness, increased bowel movements, enlarged thyroid (Goitre), increased appetite, sweating, Heart problems, menstrual irregularity, restlessness, Breathing difficulty and weight loss.
Diagnosis
Physical examination-Reveals Symptoms related to hyperthyroidism
Blood Tests – Increased TSH, T3 and T4 Levels
Radioactive iodine Uptake
Screening for thyroid auto antibodies
Treatment
The main aim of the treatment is to control the over activity of the thyroid gland.
1. Propranolol: Used to treat symptoms of increased heart rate, anxiety and sweating.
2. Prednisone: used to suppress the immune system and prevent eye irritation and tearing.
3. Anti-thyroid medications: Used to depress thyroid gland and is used to treat hyperthyroidism.
4. Radioactive iodine: Used to destroy thyroid cells and thereby controlling hyperthyroidism.
5. Surgery: Performed to remove the thyroid gland. If thyroid is removed, you will need to take thyroid hormones for the rest of your life.
Treatment Outcome (prognosis)
In most of the cases, surgery may be necessary to control the disease. Surgery or radioactive iodine therapy cures the disease completely but you will need to take thyroid hormone replacement for the life time because, otherwise it will lead to hypothyroidism which is caused by deficiency of thyroid hormones.
Complications
Complications of thyroidectomy (removal of thyroid gland) include voice problems due to nerve damage (Glosso-pharyngeal nerve), Low calcium levels as a result of damage of parathyroid glands which is often temporary, Scar on the surgical site (Neck).
Complications resulting from the disease include heart problems, eye problems and damage of the eye, Thyroid crisis- a life threatening condition due to over activity of the thyroid gland and osteoporosis- a condition resulting from calcium deficiency causing less strength of bones.
Onset of the disease
Graves disease is most common among women and the age at the onset of this disease is 20 years. It is the commonest form of hyperthyroidism.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of Graves disease includes -
psychological problems like anxiety, concentration problems, insomnia, nervousness and tremor
Physical Problems Like Breast enlargement in Men, Double vision, Exophthalmia (Protrusion of eye ball), tearing and eye irritation, Generalised weakness, increased bowel movements, enlarged thyroid (Goitre), increased appetite, sweating, Heart problems, menstrual irregularity, restlessness, Breathing difficulty and weight loss.
Diagnosis
Physical examination-Reveals Symptoms related to hyperthyroidism
Blood Tests – Increased TSH, T3 and T4 Levels
Radioactive iodine Uptake
Screening for thyroid auto antibodies
Treatment
The main aim of the treatment is to control the over activity of the thyroid gland.
1. Propranolol: Used to treat symptoms of increased heart rate, anxiety and sweating.
2. Prednisone: used to suppress the immune system and prevent eye irritation and tearing.
3. Anti-thyroid medications: Used to depress thyroid gland and is used to treat hyperthyroidism.
4. Radioactive iodine: Used to destroy thyroid cells and thereby controlling hyperthyroidism.
5. Surgery: Performed to remove the thyroid gland. If thyroid is removed, you will need to take thyroid hormones for the rest of your life.
Treatment Outcome (prognosis)
In most of the cases, surgery may be necessary to control the disease. Surgery or radioactive iodine therapy cures the disease completely but you will need to take thyroid hormone replacement for the life time because, otherwise it will lead to hypothyroidism which is caused by deficiency of thyroid hormones.
Complications
Complications of thyroidectomy (removal of thyroid gland) include voice problems due to nerve damage (Glosso-pharyngeal nerve), Low calcium levels as a result of damage of parathyroid glands which is often temporary, Scar on the surgical site (Neck).
Complications resulting from the disease include heart problems, eye problems and damage of the eye, Thyroid crisis- a life threatening condition due to over activity of the thyroid gland and osteoporosis- a condition resulting from calcium deficiency causing less strength of bones.
No comments:
Post a Comment